Medication and pharmacological aspects: effects
of high temperatures
Adverse effects of medication use at high
ambient temperatures
Medication can potentially
cause increased health problems, when used at high ambient temperatures, in a
number of ways:
Ø Altering central
thermoregulation and therefore physiological and behavioural responses.
Ø Changing cognitive
alertness, leading to, for example, increased drowsiness and reduced heat
avoidance behaviour.
Ø Changing blood pressure and cardiac output, affecting cooling
by vasodilation or increasing dizziness and fainting.
Ø Inhibiting normal sweating mechanisms for cooling by
evaporation due to anti-cholinergic effects blocking the parasympathetic
nervous system.
Ø Altering renal function and electrolyte balance, with
increased risks from dehydration and drug toxicity, or overhydration and
electrolyte imbalance.
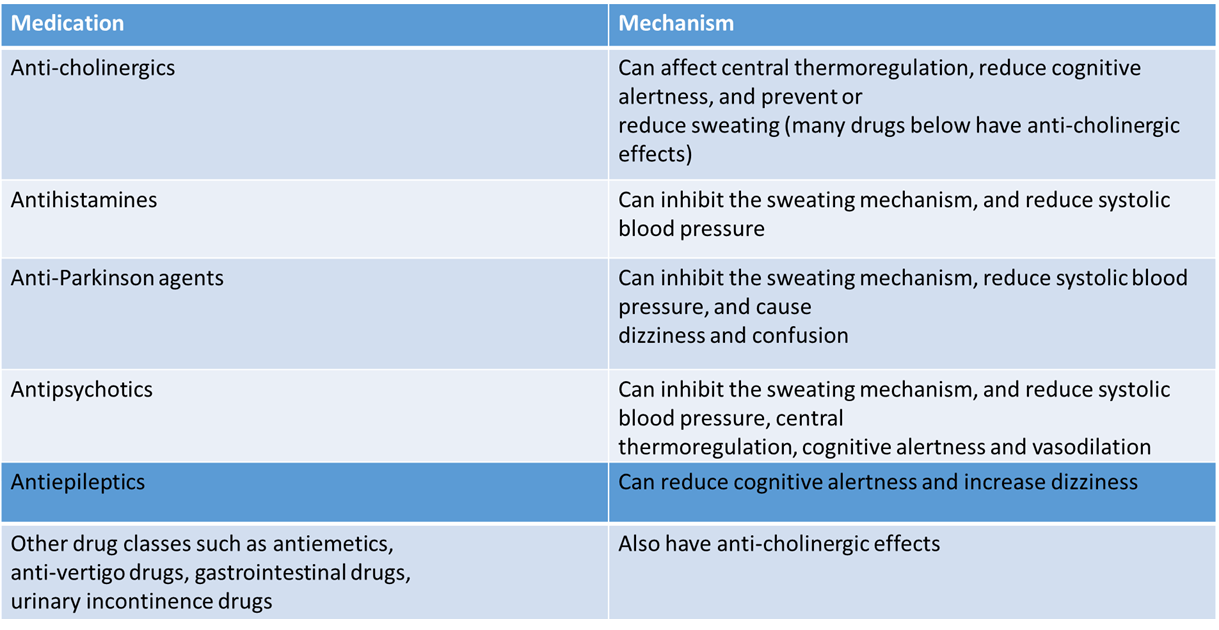
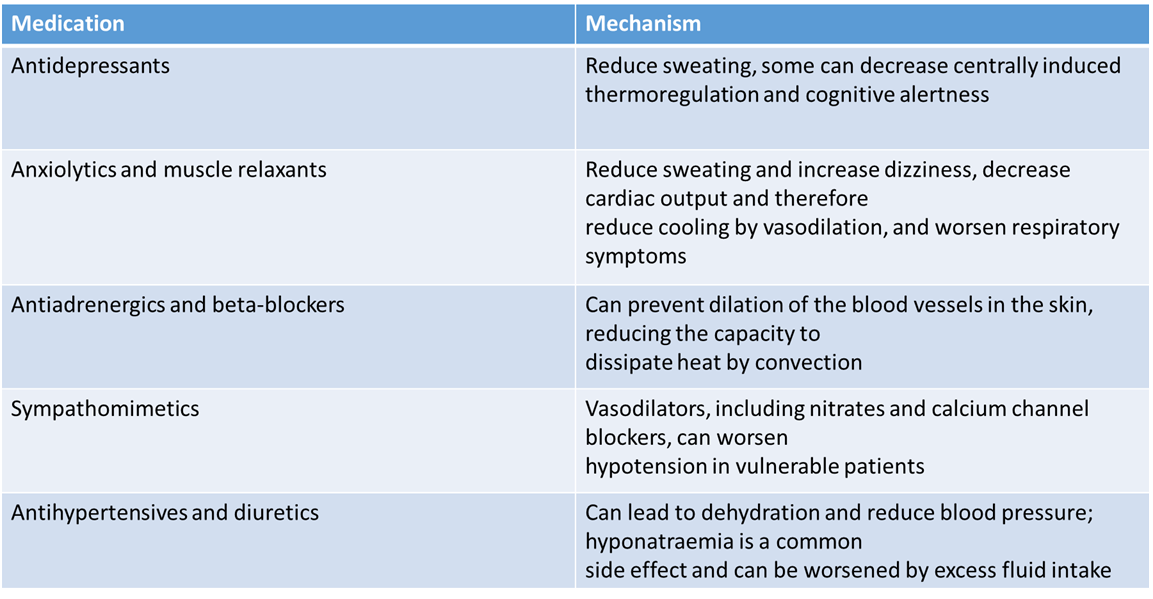
Many groups of medication can cause these effects
via a variety of mechanisms: